Click here to obtain the online quotation request form.
Internal communication (internal communication system) is an independent closed-circuit system that allows for one-way "simplex" and/or two-way "duplex" communication. The general purpose of a professional internal communication system is to simplify communication setups ranging from simple to complex (for several to thousands of users who need to continuously talk and/or listen). Two-way communication systems can operate in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode. In a half-duplex system, one party speaks while the other listens. In a full-duplex system, both parties can speak and listen simultaneously, as if engaging in a natural face-to-face conversation.
Users with different roles in specific operations can hold meetings or engage in Partyline communications together. Alternatively, users can be organized into a matrix consisting of independent groups, utilizing any one or more dedicated internal communication channels. In addition to establishing communication points, the internal communication system can also connect with third-party devices such as two-way radios, four-wire audio, telephones, television cameras, AES3 digital audio, and relay control (for signal light activation or access control), among others.
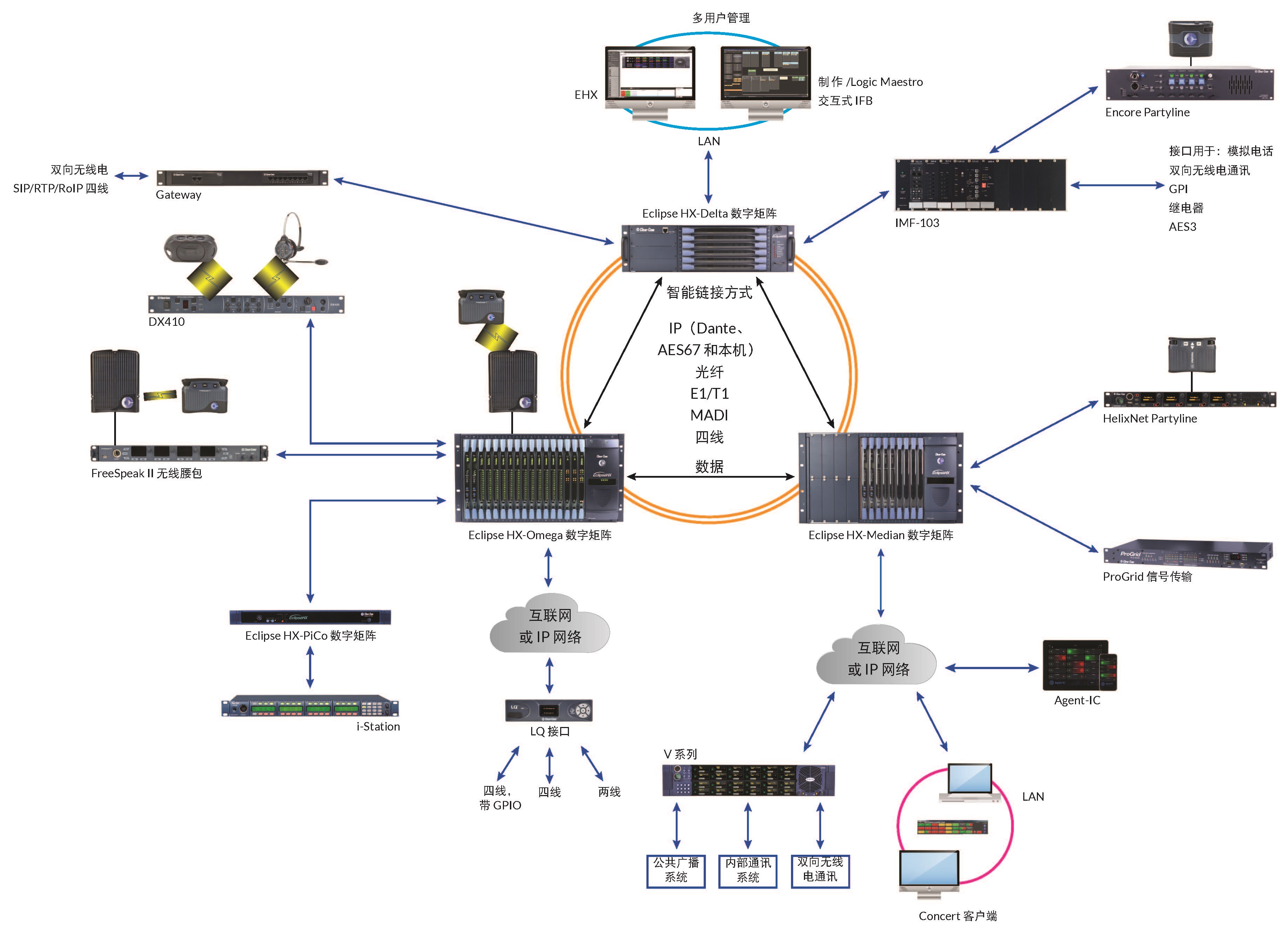
The core technology of internal communication systems can be based on one of the following platforms: two-wire/analog, four-wire/digital, wireless, or IP networks. The decision to deploy one platform over another largely depends on the requirements, environment, and budget. These internal communication platforms can operate independently or be connected to form a larger system to meet the specific needs of specialized communication workflows. Additionally, internal communication systems can connect with different communication systems as part of a multi-platform solution.
In certain applications, internal communication systems need to be distributed across different locations to support various communication points within a given workflow. Therefore, these systems can be connected in the following ways: two-wire or four-wire; MADI for short-distance connections (floor to floor); short to long-distance fiber optics within buildings; and IP networks (LAN, WAN, or the internet) for connections spanning vast areas, across towns, or distributed widely.