Recently, Amazon announced plans to livestream the Premier League in HDR format.
Prime Video will begin streaming 10 matches from the first week of December starting December 5, and will stream an additional 10 matches during the Boxing Day bank holiday period.
It has been confirmed that "some matches" will use HDR format, "providing fans with a wider color range and greater contrast, creating more vivid match visuals."
In addition, there is a new in-game match selection feature that allows fans to seamlessly switch from one match to another. Simply press the TV remote or swipe up on your mobile phone or tablet to access it. This feature eliminates the frustration of missing a few minutes of the game while switching between matches.
Amazon has also secured the services of sports broadcasters Jeff Stelling and Dan Walker. Before leaving "Soccer Saturday" at the end of last season, Stelling was a regular on Sky Sports for 30 years, while Walker previously hosted BBC's "Football Focus."
HDR (High-Dynamic Range) technology is a commonly used technique in the fields of image processing and display, aimed at providing a wider range of brightness and richer color details. By capturing and displaying more levels of brightness in images, it enhances image quality, allowing movies, pictures, and game graphics to present exceptional effects. This enables users to experience a visual experience that is closer to the real world while watching films or playing games.
What are the differences between HDR and regular SDR?
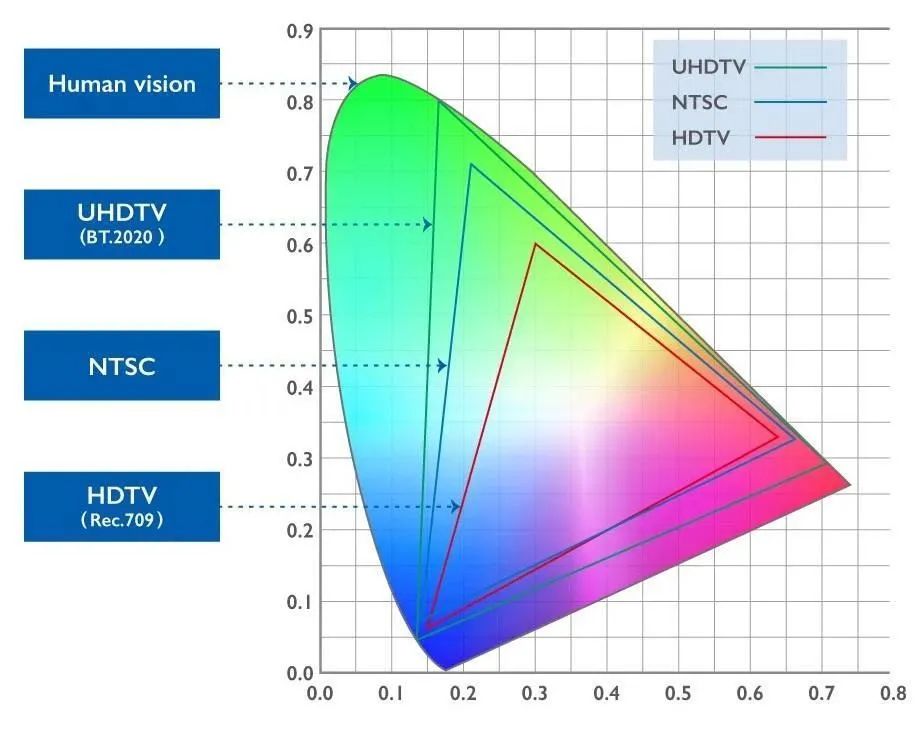
· Wider color gamut
Color space, also known as color gamut, is a concept that describes the range of colors. To put it simply, if we think of the color space as a smooth gradient ribbon, the range of colors that this ribbon can display is the concept of color space. We use the CIE 1931 color space chromaticity diagram to represent all the colors visible to the human eye. Comparing the common HDR color gamut BT-2020 (also known as Rec-2020), the NTSC color gamut customized by the National Television Standards Committee in 1953, and the SDR commonly used color gamut REC-709 (also known as sRGB), it is evident that the area of the BT-2020 color gamut is significantly larger than the others. Therefore, the richness of colors that can be displayed in HDR technology is comparatively higher.
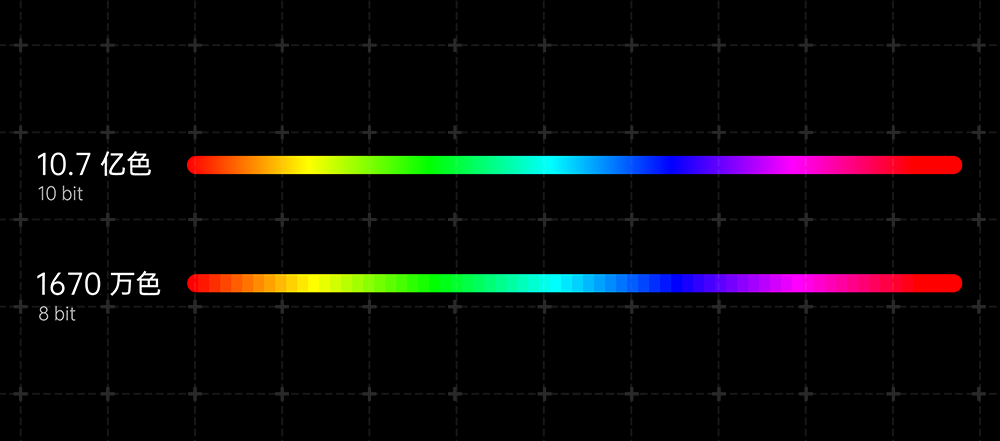
· Wider color bit depth
Color depth is a concept that describes the "fineness" of colors, generally measured in bits. Simply put, it refers to the number of colors within a unit area. The higher the value, the more detailed the image, and the smoother and more natural the color transitions. Currently, mainstream displays typically have color depths of 6bit, 8bit, and 10bit. The following image illustrates the difference between 8bit and 10bit, clearly showing that 10bit images are more detailed, while HDR technology generally adheres to a color depth of 10bit or higher. This results in more detailed image presentation and more natural transitions.
· Higher Dynamic Range
The range of brightness that the human eye can perceive can reach up to 10¹² cd/m², while traditional SDR display devices can show a range of up to 10³ cd/m². HDR can achieve up to 10⁵ cd/m², which is 100 times that of traditional SDR. Therefore, in HDR videos, we can see more details in both dark and bright areas.

Industry Standards for HDR Technology
The definition of HDR is not set by a single institution or organization, but rather by multiple different associations that establish various standards to describe it. Currently, the more common HDR standards include: HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, HLG, and HDR Vivid.
· HDR10
Launched by the Consumer Technology Association in the United States, HDR10 is an open-source, free standard. HDR10 is the foundational standard for HDR, supported by all HDR devices, and is currently the most widely adopted HDR standard. However, HDR10 uses "static metadata" technology, where the signal records absolute brightness values. This means that if your device cannot reach the required brightness, it will clip the peaks. For example, a display with a maximum brightness of 1000 nits will have to cut off any highlights above 1000 nits in a video that reaches up to 4000 nits. It is important to note that the HDR10 standard does not have strict requirements for peak luminance, which allows many hardware manufacturers to take advantage of this. Many displays claiming to support HDR10 can only play HDR content and do not achieve true HDR effects.
· Dolby Vision
Launched by Dolby Laboratories, Dolby Vision differs from HDR10 in that it uses "dynamic metadata" technology, allowing each frame to achieve more accurate maximum and minimum brightness levels. The hardware requirements are also more stringent, and each device manufacturer must pay licensing fees to Dolby Vision. To meet the Dolby Vision playback standards, several necessary conditions must be met: the content must be in a Dolby Vision-related format, and the hardware must be certified for Dolby Vision, including both the processor and the display software. Using unlicensed devices may result in playback errors and decoding issues. Despite the high licensing fees, many manufacturers have chosen to adopt Dolby Vision due to its stunning display effects. Notable brands such as LG, TCL, Philips, and Sony have included Dolby Vision support in some of their television models.
· HDR10+
HDR10+ is a collaborative initiative launched by companies such as Samsung, Amazon, Panasonic, and 20th Century Fox. It is compatible with HDR10 and offers advantages similar to Dolby Vision without charging licensing fees. HDR10+ can be seen as an upgrade to HDR10, incorporating "dynamic metadata" technology, which specifies brightness and contrast information for each frame or segment of video content.
HDR10+ EOTF is an EOTF based on the PQ curve, identical to HDR+ EOTF, allowing for the specification of real-world brightness values corresponding to video signals, thus achieving high dynamic range display. The difference between HDR10+ EOTF and HDR10 EOTF lies in the use of dynamic metadata in HDR10+ EOTF, which specifies brightness and contrast information for each frame or segment of video content, while HDR10 EOTF only uses static metadata, assigning a fixed range of brightness and contrast for the entire video. This enables HDR10+ EOTF to better adapt to different displays and scenes, enhancing the quality of HDR video.
HLG
HLG (Hybrid Log Gamma), jointly initiated by the BBC in the UK and NHK in Japan, is characterized by the absence of metadata, allowing it to be compatible with both HDR displays and the currently most popular SDR displays, with particularly good compatibility. It is a completely free standard widely used in high-definition broadcasting television systems and has gained support from some streaming services.
HDR Vivid
HDR Vivid is a new HDR standard uniquely developed in China by the UWA (formerly CUVA), led by Huawei HiSilicon technology, which supports dynamic metadata and allows for frame-level adjustments of image information. In early 2022, the National Radio and Television Administration released the industry standard "Technical Requirements for Metadata Adaptation in High Dynamic Range Television Systems" (GY/T 358-2022). The core technology of this standard has been implemented across the entire industry chain of ultra-high-definition content production, encoding, reception, decoding, and display, and is promoted under the proprietary brand name "HDR Vivid," marking it as the standard for the national broadcasting industry. In simple terms, the HDR Vivid video standard is a complete industry chain standard that encompasses all aspects of content production, encoding transmission, and terminal display. Viewers can access richer ultra-high-definition film and television content and enjoy a more immersive visual experience through video platforms and terminals that support HDR Vivid.